算法¶
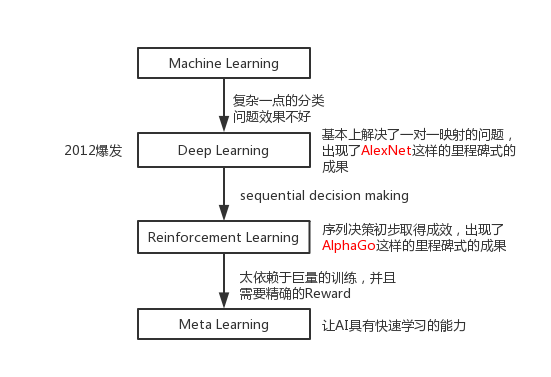
人工智能技术演变¶
在深度学习的大框架下,
终生学习Life Long Learning
少样本学习Few Shot Learning
多任务学习Multi Task Learning
多智能体学习Multi Agent Learning
学会学习Meta Learning/Learning to Learn
迁移学习Transfer Learning
Multi-class, Multi-label 以及 Multi-task 问题
- Multiclass classification
means a classification task with more than two classes; e.g., classify a set of images of fruits which may be oranges, apples, or pears. Multiclass classification makes the assumption that each sample is assigned to one and only one label: a fruit can be either an apple or a pear but not both at the same time.
- Multilabel classification
assigns to each sample a set of target labels. This can be thought as predicting properties of a data-point that are not mutually exclusive, such as topics that are relevant for a document. A text might be about any of religion, politics, finance or education at the same time or none of these.
- Multioutput-multiclass / multi-task classification
means that a single estimator has to handle several joint classification tasks. This is a generalization of the multi-label classification task, where the set of classification problem is restricted to binary classification, and of the multi-class classification task. The output format is a 2d numpy array or sparse matrix.
The set of labels can be different for each output variable. For instance a sample could be assigned “pear” for an output variable that takes possible values in a finite set of species such as “pear”, “apple”, “orange” and “green” for a second output variable that takes possible values in a finite set of colors such as “green”, “red”, “orange”, “yellow”…
This means that any classifiers handling multi-output multiclass or multi-task classification task supports the multi-label classification task as a special case. Multi-task classification is similar to the multi-output classification task with different model formulations. For more information, see the relevant estimator documentation.