Attention¶
Attention可以分成hard与soft两种模型:
hard: Attention每次移动到一个固定大小的区域
soft: Attention每次是所有区域的一个加权和
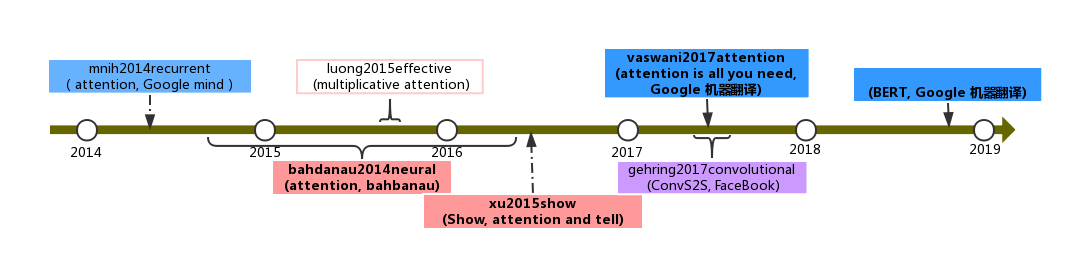
attention timeline¶
Attention mechanism 1¶
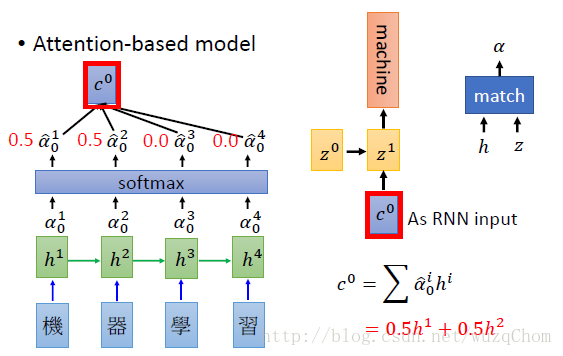
Attention-based model¶ |
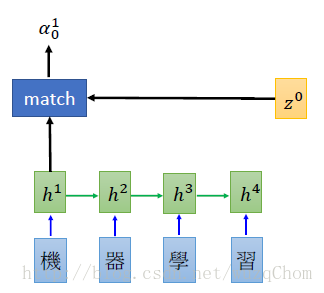
Attention mechanism¶ |
Attention机制的物理含义: 输出Target句子中某个单词和输入Source句子每个单词的对齐模型
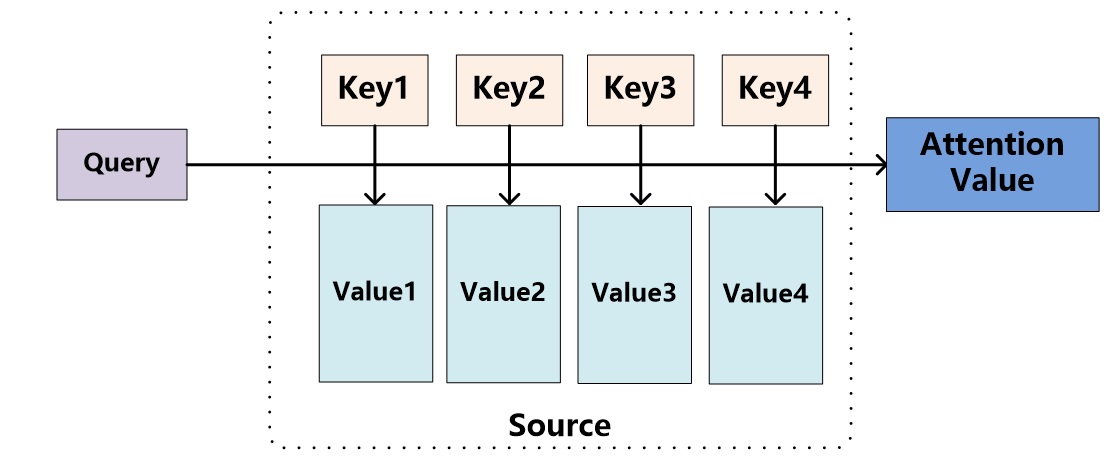
Attention 机制的本质¶
本质上Attention机制是对Source中元素的Value值进行加权求和,而Query和Key用来计算对应Value的权重系数。
根据Query和每个Key进行相似度计算得到权重
根据Query和Key计算两者的相似性或者相关性;
对前一步的值进行归一化处理
根据权重系数对Value进行加权求和
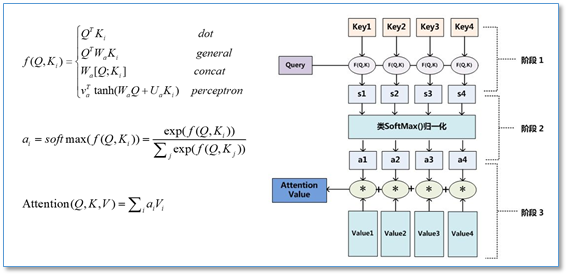
Attention calculation¶
相似度计算方法(scoring function):
感知机(perceptron/additive attention) 1 : \(\alpha = \upsilon_a^Ttanh(W_1 Q + W_2 K)\)
矩阵变换(general/multiplicative attention) 4 : \(\alpha=Q^TWK\)
点积(dot/multiplicative attention): \(\alpha = Q^TK\)
拼接(concat): \(\alpha = \upsilon_a^Ttanh(W[Q;K])\)
余弦相似度: \(\alpha = \frac{Q^TK}{ |Q||K|}\)
注解
Luong et al. 4 improved upon Bahdanau et al. 1 ’s groundwork by creating “ Global attention ”. The key difference is that with “ Global attention ”, we consider all of the encoder’s hidden states, as opposed to Bahdanau et al.’s “ Local attention ”, which only considers the encoder’s hidden state from the current time step. Another difference is that with “ Global attention ”, we calculate attention weights, or energies, using the hidden state of the decoder from the current time step only. Bahdanau et al.’s attention calculation requires knowledge of the decoder’s state from the previous time step.
attention function: context vector 和 target hidden vector 的结合方法也可以采用不同的方法
whether the previous state \(h_{t-1}\) is used instead of \(h_t\) in the scoring function as originally suggested in (Bahdanau et al., 2015)
Transformer 2¶
Motivation¶
RNNs inherently sequential nature precludes parallelization within training examples。(这里的并行指的是train的时候?)
RNN要逐步递归才能获得全局信息,因此一般要双向RNN才比较好;(RNN无法很好地学习到全局的结构信息,因为它本质是一个马尔科夫决策过程。???)
CNN(ByteNet, ConvS2S 3 )虽然能并行,但事实上只能获取局部信息,是通过层叠来增大感受野
Works¶
用attention机制代替了RNN搭建了整个模型框架。
total computational complexity per layer
parallelized
path length between long-range dependencies in the network
提出了多头注意力(Multi-headed attention),在encoder和decoder中大量的使用了多头自注意力机制(Multi-headed self-attention)。
Multi-headed attention能够从不同的表示子空间里学习相关信息
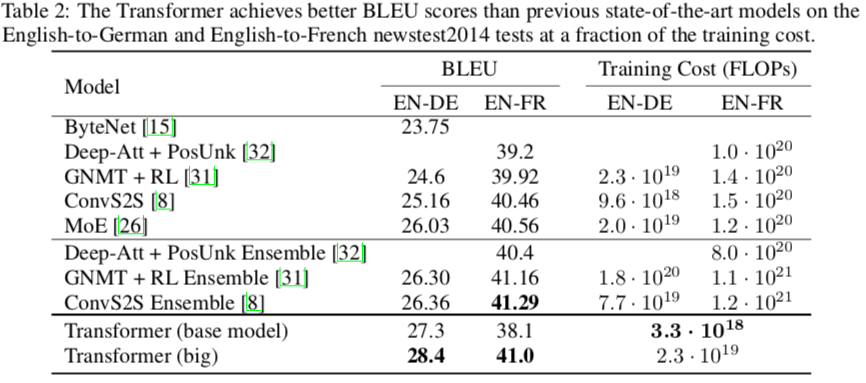
在WMT2014语料中的英德(4.5M, 37k tokens)和英法(36M, 32k word-piece)任务上取得了new state-of-art,并且训练速度比主流模型更快(8 P00 GPU)。
base model: 12h (0.4s/step, 100k)
big model: 3.5d (1.0s/step, 300k)
Model Architecture¶
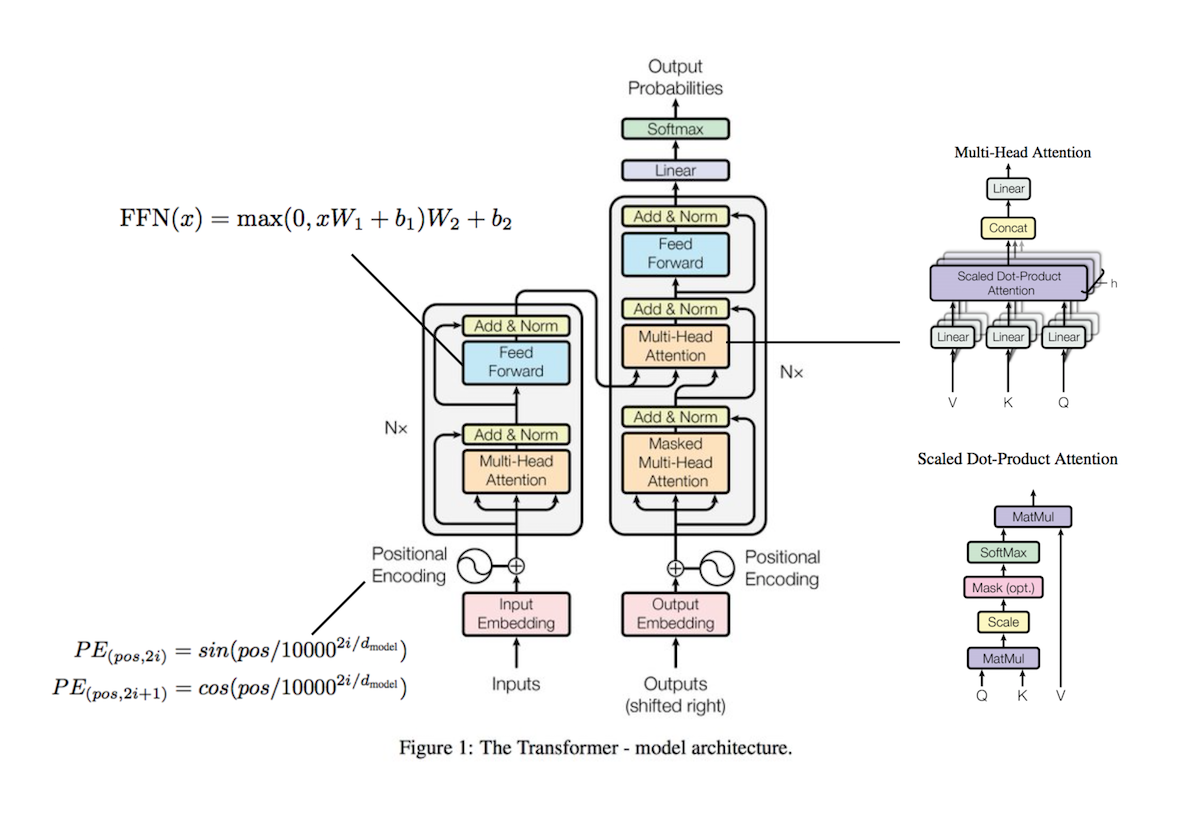
transformer model architecture¶
base model: \(N=6\), \(d_{\mathrm{model}}=512\) , \(d_{ff}=2048\) , \(h=8\) , \(d_k=d_v=64\) , 100M param for encoder
big model: \(N=6\), \(d_{\mathrm{model}}=1024\) , \(d_{ff}=4096\) , \(h=16\) , \(d_k=d_v=64\)
重要
屏蔽未来信息(decoder 中的self attention)
注解
解码层的query
按 soft attention 的思路, 解码层的关键是如何得到s(即用来和编码层做attention的query),在rnn + attention 的模型中,s与上个位置的真实label y,上个位置的s,以及当前位置的attention输出c有关,换句话说,位置i的s利用了所有它之前的真实label y信息,和所有它之前位置的attention的输出c信息。label y信息是已知的,而之前位置的c信息虽然也可以利用,但是出于并行考虑, 不能用(因为当前位置的c信息必须等它之前的c信息都计算出来)。于是我们只能用真实label y来模拟解码层的rnn。做一个masked attention(mask实现每个位置的y只与它之前的y有关),对真实label y做self-attention,这样,self-attention之后每个位置的输出综合了当前位置和它之前位置的所有y信息,即可做为s(query)。
self/intra attention¶
An attention mechanism relating different positions of a single sequence in order to compute a representation of the sequence.
=>Self Attention可以捕获同一个句子中单词之间的一些 句法特征 或者 语义特征
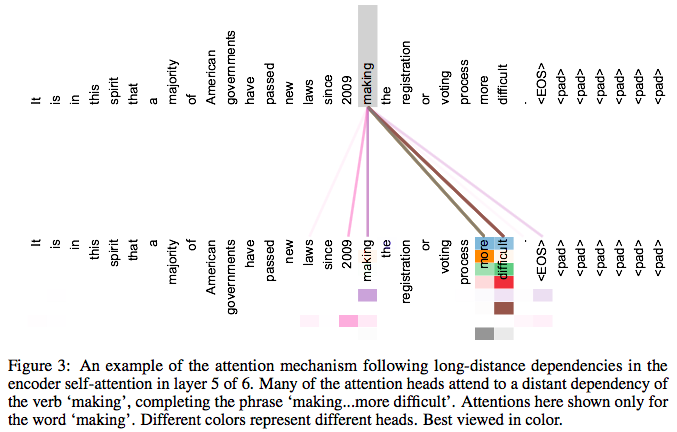
引入Self Attention后
更容易捕获句子中长距离的相互依赖的特征
如果是RNN或者LSTM,需要依序列次序计算,对于远距离的相互依赖的特征,要经过若干 timestep 的信息累积才能将两者联系起来,距离越远,有效捕获的可能性越小。而Self Attention是每个词和所有词都要计算attention,所以不管他们中间有多长距离,最大的路径长度也都只是1,可以捕获长距离依赖关系。
self-attention layers are faster than recurrent layers when the sequence length \(n\) is smaller than the representation dimensionality \(d\) 。当 \(n\) 比较大时,作者也给出了一种解决方案self-attention(restricted), 即每个词不是和所有词计算attention,而是只与邻近的 \(r\) 个词去计算attention。
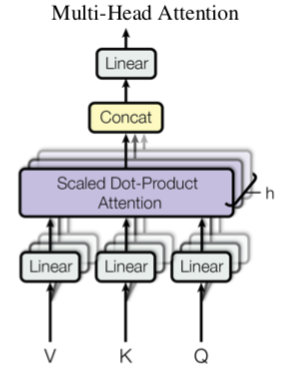
Multi-head attention¶
Multi-head attention allows the model to jointly attend to information from different representation subspaces at different positions .
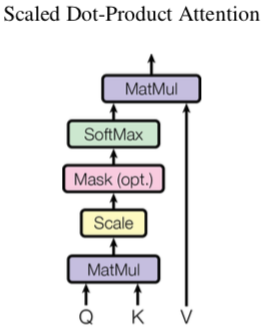
|
|
\(\mathrm{Attention}(Q, K, V) = \mathrm{softmax}(\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}})V\) |
\[\begin{split}\mathrm{MultiHead}(Q, K, V) &= \mathrm{Concat}(\mathrm{head}_1, \dots, \mathrm{head}_h)W^O \\
\mathrm{head}_i &=\mathrm{Attention}(QW_i^Q, KW_i^K, VW_i^V)\end{split}\]
|
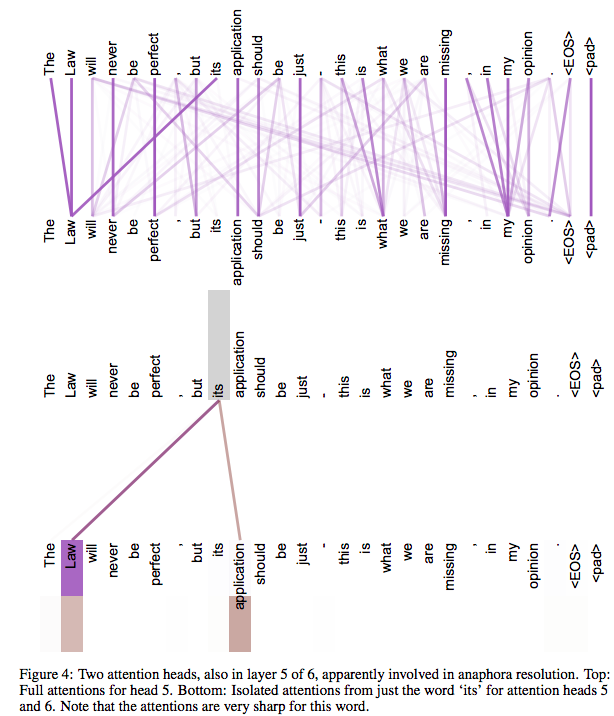
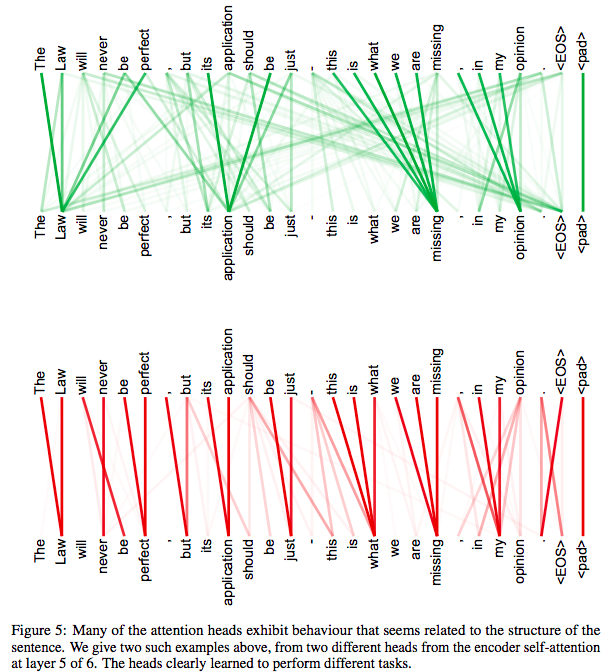
注解
dot-product vs additive attention
While the two are similar in theoretical complexity, dot-product attention is much faster and more space-efficient in practice, since it can be implemented using highly optimized matrix multiplication code.
原文还讨论了不同大小 \(d_k\) 情况下二者的表现及原因 验证
Position Embedding¶
这样的模型并不能捕捉序列的顺序! <== 如果将K,V按行打乱顺序(相当于句子中的词序打乱),那么Attention的结果还是一样的。
why
it would allow the model to easily learn to attend by relative positions, since for any fixed offset \(k\), \(PE_{pos+k}\) can be represented as a linear function of \(PE_{pos}\) .
公式 vs 训练: 效果相当
结合位置向量和词向量有几个可选方案,
拼接起来作为一个新向量
把位置向量定义为跟词向量一样大小,然后两者加起来。(chosen by Google and Facebook)
TODO¶
share param between embedding layer and pre-softmax linear transformation
代码中Multi-head attention 按Q、K、V最后一维分解怎么理解?
这里其实是为了实现做h次attention,每次先将Q、K、V映射到d_k = d_v = d_model/h维,然后进行attention计算。这种写法只是为了方便,将 h 次映射的参数放在一起实现
理解
encoder 通过self attention 获得能够体现 句法特征 或者 语义特征 的表征,decoder做语法对齐,同时也要考虑自身的*句法特征* 或者 语义特征 。多层即从低层向高层抽象
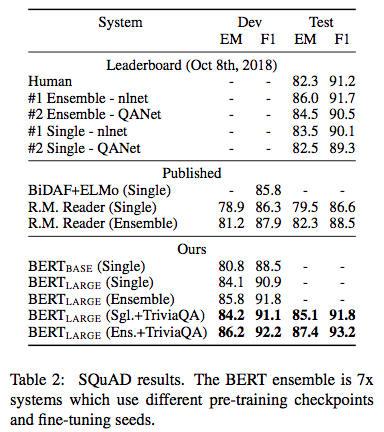
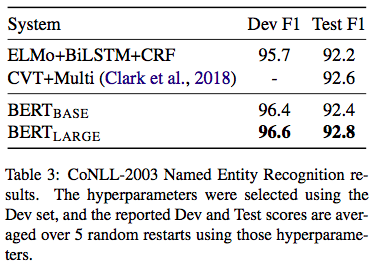
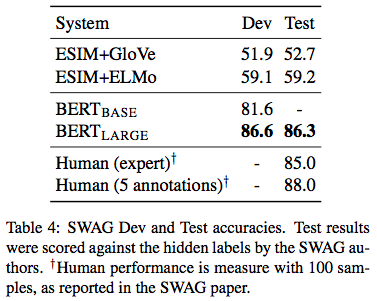
BERT 5¶
Motivation¶
NLP领域通常只会使用预训练词嵌入向量编码词汇间的关系,因此也就没有一个能用于整体模型的预训练方法(–> 需要大量示例)。而语言模型有作为整体预训练模型的潜质,它能由浅到深抽取语言的各种特征,并用于机器翻译、问答系统和自动摘要等广泛的 NLP 任务。
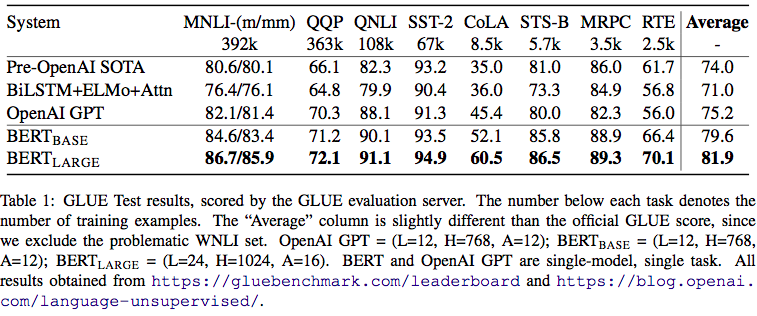
预训练的语言模型可以在一大批 NLP 任务中达到当前最优水平
ULMFiT、ELMo 和 OpenAI transformer 最新进展的核心是一个关键的范式转变:从仅仅初始化模型的第一层到用分层表示对整个模型进行预处理。
局限在于标准语言模型是单向的, 无法泛化使用到各种不同的NLP task 中
Works¶
BERT: a multi-layer bidirectional Transformer encoder
预训练目标
MLM: deep bidirectionality
NSP: understanding the relationship between two text sentences
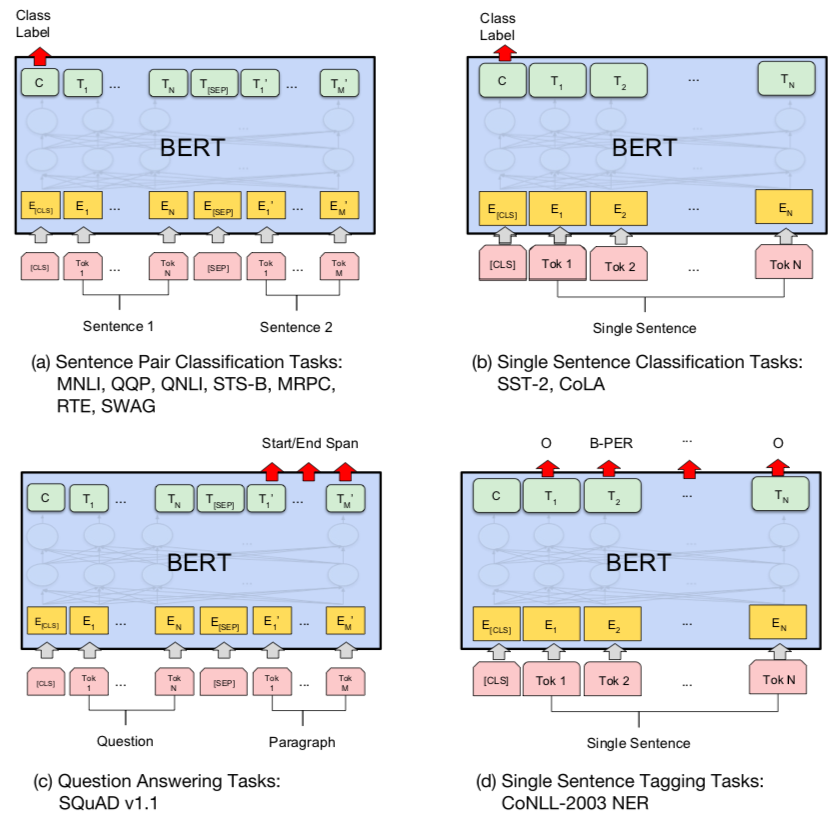
预训练的 BERT 可以通过fine-tune,适用于广泛任务的最先进模型的构建; 也可以用于feature-based approach
Model Architecture¶
BASE: L=12, H=768, A=12, Total Parameters=110M
LARGE: L=24, H=1024, A=16, Total Parameters=340M
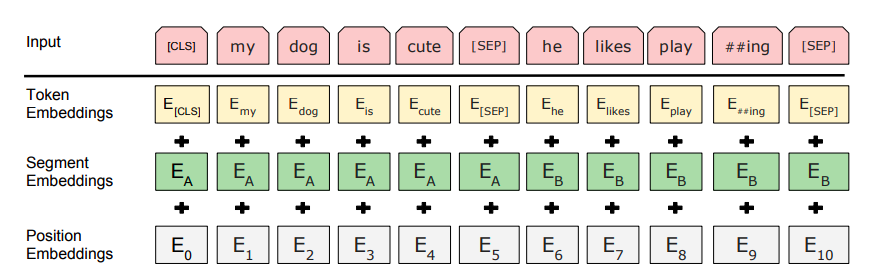
token: wordpiece embedding
segment: A, B
position: learned positional embedding, 512
Pretrain¶
- Data
BooksCorpus (800M words) + English Wikipedia (2,500M words)
batch size of 256 sequences (256 sequences * 512 tokens = 128,000 tokens/batch), 1M step
BASE: 4 Cloud TPUs in Pod configuration (16 TPU chipstotal), 4d
LARGE: 16 Cloud TPUs (64 TPU chips total), 4d
MLM¶
Masking some percentage(15%) of the input tokens at random, and then predicting only those masked tokens.
a mismatch between pre-training and fine-tuning
80% of the time: Replace the word with the [MASK] token
10% of the time: Replace the word with a random word
10% of the time: Keep the word un-changed
=> distributional contextual representation of every token
difference between distributed representation and distributional representation
15% mask => more pre-training steps may be required for the model to converge.
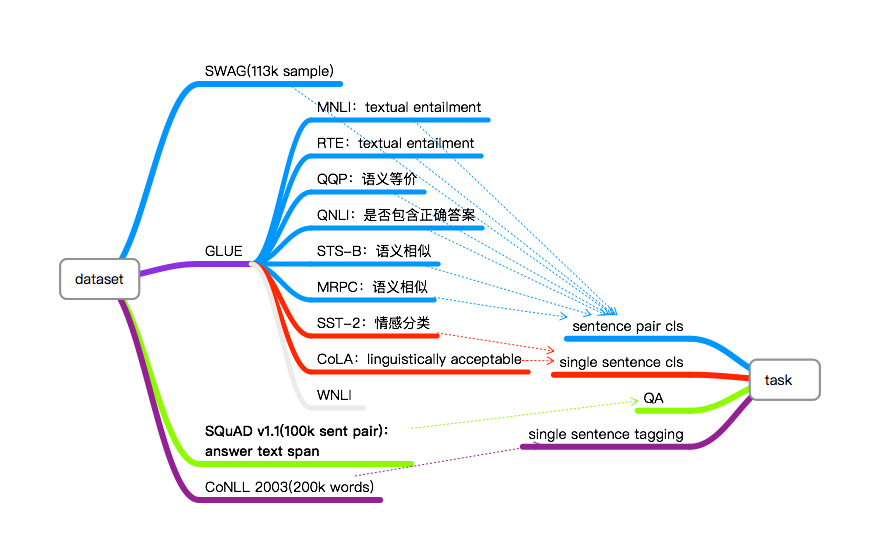
应用到我们的项目中¶
长度
order: Transformer 不使用Position embedding
- 1(1,2,3)
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate[J] . arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.0473, 2014.
- 2
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, et al. Attention is all you need[J] . Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 5998-6008.
- 3
Gehring J, Auli M, Grangier D, et al. Convolutional sequence to sequence learning[J] . arXiv preprint arXiv:1705.03122, 2017.
- 4(1,2)
Luong M T, Pham H, Manning C D. Effective approaches to attention-based neural machine translation[J] . arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.04025, 2015.
- 5
BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding